Autonomous vehicles are no longer a distant dream—they are rapidly transforming the transportation landscape. Research on autonomous vehicles has accelerated over the past decade, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), sensor technology, and machine learning algorithms. These innovations have made self-driving cars increasingly capable of navigating complex urban environments safely and efficiently. From companies like Waymo, Tesla, and Cruise, to academic institutions conducting cutting-edge studies, the field is witnessing an unprecedented surge in technological breakthroughs.
The importance of research on autonomous vehicles extends beyond convenience. Self-driving technology promises to significantly reduce traffic accidents caused by human error, improve fuel efficiency, and provide mobility solutions for people who are unable to drive. Governments, automotive companies, and tech startups are investing billions of dollars into research and development to bring these vehicles to public roads safely.
The evolution of autonomous vehicles can be traced through various milestones. Early experiments focused on driver assistance features, such as adaptive cruise control and lane-keeping systems. Over time, researchers have progressed to fully autonomous prototypes capable of handling complex traffic scenarios with minimal human intervention. Today, self-driving cars are undergoing rigorous simulation testing and real-world trials, showcasing the growing reliability of this technology.http://futuretechfrontier.com
In this article, we will explore the latest research on autonomous vehicles, including the technology behind them, industry applications, safety considerations, challenges, and future trends. Whether you are a technology enthusiast, a student, or an industry professional, understanding these insights will provide a comprehensive view of how autonomous vehicles are shaping the future of transportation.
What Are Autonomous Vehicles?
Autonomous vehicles, often referred to as self-driving cars, are vehicles equipped with technology that allows them to navigate and operate without direct human control. These vehicles rely on a combination of sensors, AI algorithms, and real-time data processing to make decisions on the road, such as steering, braking, and acceleration. Understanding what autonomous vehicles are is critical for appreciating the scope of research on autonomous vehicles and their potential impact on society.
Levels of Autonomy in Vehicles (SAE Levels 0-5)
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) defines six levels of vehicle automation, ranging from Level 0 (no automation) to Level 5 (full automation). These levels are widely used in research on autonomous vehicles to categorize the complexity and capabilities of self-driving systems.
- Level 0 – No Automation: The driver is fully responsible for all driving tasks. Examples include traditional cars without advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
- Level 1 – Driver Assistance: Features like adaptive cruise control or lane-keeping assist help the driver, but human control is still required.
- Level 2 – Partial Automation: The vehicle can handle certain tasks, such as steering and acceleration simultaneously, but the driver must remain attentive.
- Level 3 – Conditional Automation: The car can manage most driving tasks in specific conditions, but human intervention may be needed when the system encounters complex scenarios.
- Level 4 – High Automation: Vehicles can operate without human input within defined environments or geofenced areas, such as a specific urban district.
- Level 5 – Full Automation: The car is capable of driving anywhere, in any condition, without human intervention. This level represents the ultimate goal of most autonomous vehicle research.
Key Benefits of Autonomous Vehicles
The research and development of autonomous vehicles are not only technological pursuits—they aim to bring tangible benefits for society and businesses:
- Enhanced Road Safety: Human error accounts for approximately 94% of traffic accidents. Autonomous systems can reduce accidents by reacting faster than human drivers.
- Improved Traffic Efficiency: Self-driving cars can communicate with each other and traffic infrastructure to optimize traffic flow, reducing congestion.
- Accessibility: Elderly, disabled, or visually impaired individuals gain greater mobility with autonomous vehicles.
- Environmental Impact: Autonomous vehicles can drive more efficiently, leading to lower fuel consumption and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
- Economic Benefits: From ride-sharing services to logistics, automation in vehicles can lower operational costs for companies.
Variations in Research Focus
Research on autonomous vehicles is diverse, ranging from technological innovation to social and regulatory studies:
- Technological Research: Focuses on AI, sensors, edge computing, and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication.
- Safety Research: Studies accident prevention, risk assessment, and fail-safe systems.
- Policy and Ethics Research: Examines regulations, liability, and moral decision-making algorithms.
- Market Research: Analyzes adoption trends, consumer behavior, and economic impact.
This foundational understanding of what autonomous vehicles are, their levels of autonomy, and key benefits provides the context needed to dive deeper into the technologies and advancements driving the industry.
Recent Research and Technological Advancements in Autonomous Vehicles
The rapid evolution of autonomous vehicles is powered by cutting-edge research and technological breakthroughs. From artificial intelligence to advanced sensor systems, these innovations are enabling self-driving cars to operate safely and efficiently in increasingly complex environments. Understanding these advancements is key to grasping the current state and future potential of autonomous vehicle research.
AI and Machine Learning in Self-Driving Cars
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are at the heart of autonomous vehicle functionality. AI systems analyze massive amounts of data from sensors and cameras to make real-time driving decisions. Deep learning algorithms enable vehicles to recognize objects, predict pedestrian movements, and respond to dynamic traffic conditions.
- Computer Vision: Allows the vehicle to identify lanes, road signs, obstacles, and other vehicles.
- Predictive Analytics: AI predicts the behavior of other drivers, cyclists, and pedestrians, improving safety.
- Reinforcement Learning: Vehicles learn optimal driving strategies over time through simulations and real-world trials.
Case Study: Waymo’s autonomous vehicles rely heavily on AI-powered perception systems, which have collectively driven over 20 million miles in real-world conditions, improving their decision-making algorithms continually.
Sensor Technologies in Autonomous Vehicles
Research on autonomous vehicles heavily focuses on sensor integration to perceive the surrounding environment accurately. Modern self-driving cars typically use a combination of:
- LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): Generates precise 3D maps of the environment, detecting obstacles and measuring distances.
- RADAR (Radio Detection and Ranging): Tracks the speed and movement of objects, even in poor visibility.
- Ultrasonic Sensors: Monitor close-range obstacles for parking and low-speed maneuvers.
- Cameras: Capture visual data for lane recognition, traffic signs, and pedestrian detection.
Sensor Fusion: By combining data from multiple sensors, autonomous vehicles achieve higher accuracy and reliability, compensating for the limitations of any single sensor.
Fact: Studies indicate that sensor fusion can reduce object detection errors by up to 50%, a major breakthrough in autonomous vehicle safety.
Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication
V2X communication is a growing research area that allows vehicles to exchange information with each other (V2V) and surrounding infrastructure (V2I).
- Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V): Enables cars to communicate hazards, braking events, and traffic conditions instantly.
- Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I): Traffic lights, road signs, and smart sensors transmit real-time data to vehicles for optimized routing.
Impact: Research shows that integrating V2X technology can reduce intersection collisions by up to 80%, a major advancement for urban self-driving deployments.
Simulation and Testing for Autonomous Vehicles
Before autonomous vehicles hit public roads, extensive simulation and testing are critical. Research uses both virtual environments and controlled real-world conditions to train AI systems:
- Simulation Environments: Allow testing of millions of driving scenarios safely, including rare or dangerous situations.
- Real-World Trials: Autonomous cars are tested on city streets and highways, with monitoring systems recording performance.
- Digital Twins: Create virtual replicas of vehicles to predict real-world behavior under varying conditions.
Example: Tesla’s fleet collects data from millions of miles driven, feeding machine learning algorithms to improve autopilot performance continually.
Cloud and Edge Computing for Autonomous Vehicles
Modern autonomous vehicles rely on cloud and edge computing to process enormous volumes of data in real-time:
- Cloud Computing: Supports large-scale data storage, software updates, and advanced analytics for fleet management.
- Edge Computing: Processes data locally on the vehicle for immediate decision-making, reducing latency in critical situations.
Fact: Combining cloud and edge computing allows self-driving cars to respond to hazards within milliseconds, which is crucial for passenger safety.
Summary of Technological Advancements
| Technology | Role in Autonomous Vehicles | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| AI & Machine Learning | Decision-making, perception, predictive analytics | Safer, smarter driving |
| LIDAR, RADAR, Cameras | Object detection, mapping, obstacle avoidance | Higher accuracy, sensor redundancy |
| V2X Communication | Vehicle & infrastructure data sharing | Reduced collisions, optimized traffic |
| Simulation & Testing | Virtual and real-world scenario training | Improved safety and reliability |
| Cloud & Edge Computing | Data processing & software updates | Faster response, scalable fleet management |
These technologies, collectively, are the backbone of current research on autonomous vehicles, enabling vehicles to move from assisted driving toward full autonomy.
Industry Applications and Use Cases of Autonomous Vehicles
The practical applications of autonomous vehicles are expanding rapidly as research on autonomous vehicles moves from laboratories to real-world deployment. Self-driving technology is not limited to personal cars—it is transforming industries ranging from transportation to logistics, public services, and even agriculture. Understanding these use cases highlights the tangible benefits and economic potential of autonomous vehicles.
Autonomous Vehicles in Passenger Transportation
Self-driving cars are poised to revolutionize urban mobility:
- Self-Driving Taxis: Companies like Waymo, Cruise, and AutoX are testing fleets of autonomous taxis in cities such as Phoenix and San Francisco. These services reduce the need for human drivers and can provide 24/7 mobility.
- Ride-Sharing Services: Integration with ride-hailing apps allows autonomous vehicles to optimize routes, reduce wait times, and improve fuel efficiency.
- Urban Mobility Planning: Research shows that autonomous vehicles can reduce congestion in urban centers by up to 30% through optimized routing and coordinated traffic flow.
Case Study: Waymo’s autonomous ride-hailing service has completed over 20 million miles of autonomous driving, demonstrating safety improvements and efficiency gains.
Autonomous Vehicles in Logistics and Delivery
Autonomous vehicles are reshaping the logistics and delivery sectors:
- Self-Driving Trucks: Companies like TuSimple and Kodiak Robotics are developing autonomous trucks for long-haul freight, improving delivery efficiency and reducing driver fatigue.
- Delivery Robots: Small autonomous delivery vehicles and drones are being used for last-mile delivery, particularly in urban areas.
- Cost and Efficiency Benefits: Research indicates that autonomous freight transport could reduce operational costs by up to 40%, while increasing delivery speed and reliability.
Fact: UPS has been testing autonomous delivery vans and predicts these vehicles could handle up to 10% of their last-mile deliveries, especially in high-density areas.
Autonomous Vehicles in Public Services
Government and public service applications of autonomous vehicles are growing:
- Emergency Response Vehicles: Autonomous ambulances and fire trucks can navigate traffic more efficiently, potentially saving lives.
- Public Transit Systems: Cities are piloting autonomous buses and shuttles, improving accessibility and reducing operational costs.
- Research Insight: Studies suggest autonomous public transport could reduce operational costs by 15–25%, while improving service reliability and consistency.
Autonomous Vehicles in Agriculture and Industrial Use
Beyond roads, autonomous vehicle research is expanding into industrial and agricultural sectors:
- Self-Driving Tractors: Autonomous tractors and harvesters enable precision farming, reducing labor costs and increasing crop yields.
- Mining Vehicles: Heavy machinery in mining operations is becoming autonomous, improving safety in hazardous environments.
- Warehouse Automation: Autonomous forklifts and carts optimize warehouse logistics, reducing human error and operational costs.
Example: John Deere has developed autonomous tractors that use GPS-guided precision farming, increasing efficiency while reducing fuel and labor costs.
Summary of Industry Applications
| Sector | Autonomous Vehicle Application | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Passenger Transport | Self-driving taxis, ride-sharing, urban shuttles | Reduced congestion, 24/7 mobility, lower costs |
| Logistics & Delivery | Autonomous trucks, delivery robots | Faster delivery, reduced operational costs, safer freight transport |
| Public Services | Emergency vehicles, autonomous buses | Improved response times, lower costs, enhanced accessibility |
| Agriculture & Industry | Autonomous tractors, mining machinery, warehouse robots | Higher efficiency, reduced labor, improved safety |
These examples show how research on autonomous vehicles is not only advancing technology but also transforming multiple industries. Companies and governments are leveraging self-driving technology to improve efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness across diverse sectors.
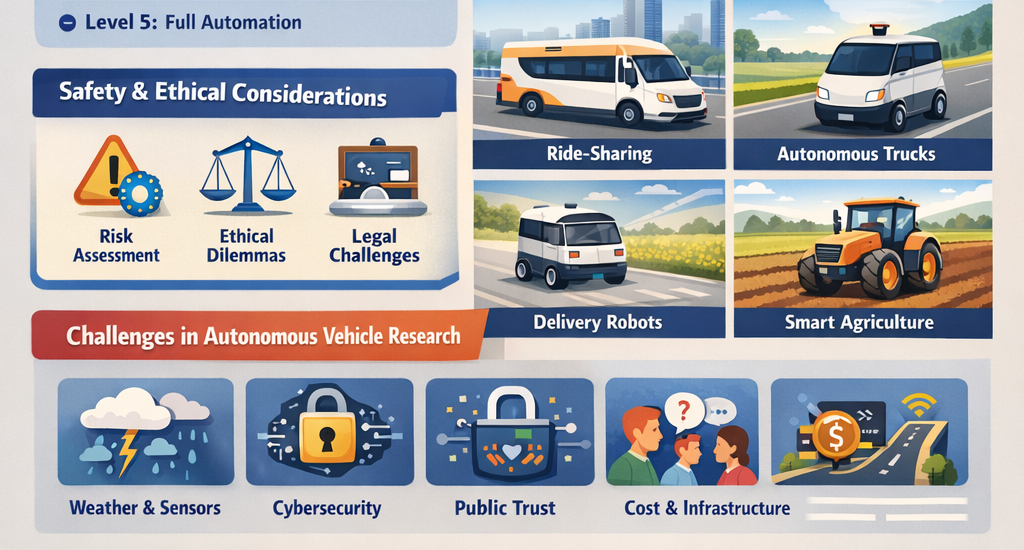
Safety, Ethics, and Legal Considerations in Autonomous Vehicle Research
As autonomous vehicles move closer to widespread adoption, research on autonomous vehicles increasingly focuses on safety, ethical dilemmas, and legal frameworks. These considerations are critical because they determine public trust, regulatory approval, and the overall success of self-driving technology.
Safety Concerns and Risk Assessment
Safety is the most significant factor in autonomous vehicle research. Despite advancements, self-driving cars face challenges in unpredictable environments, including:
- Accident Prevention: Autonomous vehicles use AI, sensors, and V2X communication to reduce accidents caused by human error, which accounts for 94% of road crashes globally.
- Fail-Safe Systems: Redundant sensors and backup algorithms ensure vehicles remain operational if a component fails.
- Extreme Conditions: Research shows autonomous vehicles must navigate adverse weather, such as heavy rain, snow, or fog, where sensor performance can degrade.
Example: Volvo and Waymo have developed extensive testing protocols that simulate over 10 million virtual miles, helping AI systems handle rare but critical driving scenarios safely.
Ethical Considerations in Decision-Making
Autonomous vehicles must make split-second decisions in complex situations, raising ethical questions:
- Trolley Problem Scenarios: How should a vehicle react when an accident is unavoidable? Should it prioritize passenger safety over pedestrians?
- Programming Morality: Developers must encode decision-making frameworks for autonomous vehicles, balancing ethical principles, legal compliance, and societal norms.
- Bias in AI: Researchers work to ensure AI algorithms make fair and unbiased decisions, avoiding discrimination based on location, demographic, or road conditions.
Fact: A survey by the MIT Media Lab found that 76% of respondents want self-driving cars programmed to minimize overall harm, even if it endangers passengers in rare situations.
Legal and Regulatory Challenges
Regulations are essential to integrate autonomous vehicles into public roads safely:
- Liability in Accidents: Determining fault is complex when a vehicle operates autonomously. Manufacturers, software developers, and owners may share responsibility.
- Global Regulations: Countries differ in autonomous vehicle laws. The US allows state-level regulations, while the EU focuses on harmonized safety standards.
- Insurance Considerations: Policies must adapt to cover software malfunctions, cyberattacks, and shared liability scenarios.
Example: In 2022, a Tesla autopilot incident prompted debates over whether the software or the driver should be held accountable, highlighting the need for clear legal frameworks.
Summary of Safety, Ethics, and Legal Considerations
| Consideration | Key Focus | Research Insights |
|---|---|---|
| Safety | Accident prevention, fail-safe systems, extreme conditions | Sensor redundancy and AI testing reduce risk significantly |
| Ethics | Decision-making, moral dilemmas, AI bias | Trolley-problem studies guide ethical AI programming |
| Legal | Liability, regulations, insurance | Harmonized laws and clear policies are essential for adoption |
Addressing these factors is crucial for the successful deployment of autonomous vehicles. Researchers, regulators, and industry stakeholders must collaborate to ensure self-driving technology is not only technologically advanced but also safe, ethical, and legally compliant.
Challenges in Autonomous Vehicle Research
Despite rapid technological advancements, research on autonomous vehicles faces several significant challenges. These hurdles span technical limitations, cybersecurity threats, public acceptance, and infrastructure requirements. Overcoming these challenges is critical to making fully autonomous vehicles a practical reality.
Technical Challenges
Autonomous vehicles must operate reliably in diverse and unpredictable environments, which presents several technical obstacles:
- Sensor Limitations: LIDAR, RADAR, and cameras can struggle in adverse weather conditions such as heavy rain, fog, or snow. Maintaining accurate perception in these scenarios is a major research focus.
- Complex Urban Environments: Navigating dense city streets, construction zones, and unpredictable pedestrian behavior requires highly sophisticated AI algorithms.
- Edge Case Scenarios: Rare but critical driving situations (e.g., a child running into the street) must be anticipated and safely managed by autonomous systems.
Fact: Studies estimate that fully autonomous systems need to encounter billions of driving miles in diverse conditions to achieve reliability comparable to human drivers.
Data and Cybersecurity Challenges
Autonomous vehicles rely on vast amounts of data for AI decision-making, making cybersecurity a crucial concern:
- Hacking Risks: Vehicles connected to networks are vulnerable to cyberattacks that could compromise safety.
- Data Privacy: Collecting real-time data on passengers, vehicles, and surroundings raises privacy concerns.
- Software Updates: Ensuring secure, over-the-air updates without introducing vulnerabilities is a key research area.
Case Study: In 2015, researchers remotely hacked a Jeep Cherokee, demonstrating the importance of cybersecurity in connected vehicles. Autonomous vehicle research now heavily focuses on secure architecture and encryption protocols.
Public Acceptance and Trust
Even with advanced technology, public skepticism remains a significant barrier:
- Fear of Losing Control: Many people are hesitant to trust vehicles that operate without human input.
- Ethical Concerns: Passengers and pedestrians may worry about AI decision-making in life-threatening scenarios.
- Education and Awareness: Studies suggest that increasing public exposure to autonomous vehicles in controlled environments can boost trust and acceptance.
Stat: A 2023 survey by AAA found that 55% of Americans are uncomfortable riding in a fully autonomous vehicle, highlighting the need for education and transparent communication.
Cost and Infrastructure Challenges
Deploying autonomous vehicles at scale requires significant investment in both technology and infrastructure:
- High Development Costs: Research, prototyping, and testing for autonomous systems are expensive, often running into billions of dollars for large-scale projects.
- Road Infrastructure: Autonomous vehicles require smart roads, sensors, and V2I communication systems to operate safely and efficiently.
- Integration with Existing Traffic: Mixed environments with human drivers, cyclists, and pedestrians add complexity.
Example: Singapore has invested heavily in smart infrastructure and connected roadways to facilitate testing and deployment of autonomous vehicles, serving as a model for urban implementation.
Summary of Research Challenges
| Challenge Category | Key Issues | Research Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Technical | Sensor limitations, edge cases, complex environments | AI robustness, sensor fusion, scenario testing |
| Cybersecurity & Data | Hacking, data privacy, software updates | Secure architecture, encryption, privacy compliance |
| Public Acceptance | Trust, fear, ethical concerns | Awareness campaigns, transparent communication |
| Infrastructure & Cost | High development costs, smart roads, mixed traffic | Urban planning, V2I networks, cost optimization |
Addressing these challenges is essential for moving from experimental autonomous vehicles to safe, widespread adoption. Ongoing research is targeting these issues to ensure reliability, security, and societal acceptance.