Introduction
Innovation in technology is the driving force behind the world’s progress, shaping the way we live, work, and interact. From the devices in our pockets to advanced medical tools, technological innovation influences nearly every aspect of modern life. But what exactly does innovation in technology mean, and why is it so important?
At its core, innovation in technology refers to the process of developing new technologies, improving existing systems, or finding creative solutions to challenges using technology. This can range from incremental improvements to radical breakthroughs that completely change industries. For example, the evolution of smartphones, the rise of artificial intelligence, and the development of renewable energy solutions are all examples of technological innovation transforming society.
The importance of innovation in technology cannot be overstated. It drives economic growth, enhances productivity, improves healthcare, and even addresses environmental challenges. Businesses that embrace tech innovations can gain a competitive edge, while governments and organizations rely on emerging technology to solve complex societal problems.http://futuretechfrontier.com
In this article, we will explore the many dimensions of innovation in technology, including its types, impacts, emerging trends, and how individuals, companies, and governments can foster a culture of innovation. By understanding these concepts, readers can better appreciate the transformative power of technology and how it shapes the future.
Understanding Innovation in Technology
Definition of Technological Innovation
Technological innovation refers to the process of creating or improving technologies to solve problems, improve efficiency, or create new opportunities. Unlike simple technological tools, which may exist for convenience, technological innovation involves creative thinking, research, and practical implementation.
There are three main types of technological innovation:
- Incremental Innovation – Small, continuous improvements to existing technology. For example, upgrades to smartphones or software updates.
- Disruptive Innovation – Innovations that completely change the way industries operate. Autonomous vehicles and blockchain technology are classic examples.
- Radical Innovation – Groundbreaking technologies that create entirely new markets, such as the first personal computer or CRISPR gene-editing technology.
Each type of innovation plays a role in shaping industries, influencing how businesses and individuals interact with technology. Understanding these categories helps organizations plan research and development (R&D) strategies effectively.
Importance of Innovation in Technology
Innovation in technology is not just about creating new gadgets; it is essential for societal growth and development. Here’s why it matters:
- Economic Impact: Innovative technologies create new industries, improve productivity, and generate jobs. For example, AI and automation have spurred a growing demand for data scientists, AI specialists, and robotics engineers.
- Healthcare Advancements: Medical technologies, such as AI-driven diagnostics, robotic surgery, and telemedicine, have revolutionized patient care and accessibility.
- Global Competitiveness: Countries and companies that prioritize innovation stay ahead in the global economy. For instance, nations investing heavily in renewable energy technologies are leading the transition to a sustainable future.
- Problem Solving: Technological innovation addresses complex challenges like climate change, energy shortages, and resource management through creative, tech-driven solutions.
In essence, innovation in technology drives progress, improves quality of life, and provides a competitive advantage to those who embrace it.
History of Innovation in Technology
Innovation in technology has a long and fascinating history. Understanding past breakthroughs helps us predict future trends. Key milestones include:
| Era | Innovation | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 18th Century | Industrial Revolution | Mechanized production, increased productivity |
| 20th Century | Computers & Internet | Digitalization of work, communication, and commerce |
| 21st Century | Smartphones & AI | Global connectivity, automation, and smart solutions |
Case Study: The invention of the internet transformed communication, commerce, and entertainment globally. What began as a simple network for academics eventually evolved into a platform driving innovation in nearly every industry.
Historical trends show that technological innovation accelerates over time, with modern breakthroughs happening faster than ever before, thanks to AI, cloud computing, and global collaboration.
Types of Innovation in Technology
Innovation in technology comes in many forms, each shaping industries and society differently. Understanding these types helps businesses, governments, and individuals leverage the right strategies for growth and development.
Product Innovation
Product innovation refers to the creation of new or improved products that offer unique features or better performance. These innovations often enhance user experience, solve existing problems, or introduce entirely new functionalities.
Examples of product innovation:
- Smartphones: Continuous upgrades in processing power, cameras, and AI capabilities.
- Wearable devices: Fitness trackers and smartwatches integrating health monitoring.
- AR/VR gadgets: Immersive devices transforming gaming, education, and professional training.
Impact: Product innovation not only improves consumer choice but also drives market competition. Companies that invest in product R&D often dominate their industries and set trends for competitors.
Process Innovation
Process innovation focuses on improving the methods and procedures used to create or deliver products and services. It emphasizes efficiency, cost reduction, and consistency while maintaining quality.
Examples of process innovation:
- Cloud computing: Allows companies to scale operations without heavy infrastructure costs.
- AI-powered automation: Streamlines repetitive tasks, reducing errors and time spent.
- 3D printing: Transforms manufacturing processes, enabling rapid prototyping and cost-effective production.
Impact: By optimizing processes, organizations can increase productivity, reduce waste, and accelerate delivery times, giving them a significant competitive advantage.
Disruptive Innovation
Disruptive innovation radically changes existing markets or creates entirely new ones. Unlike incremental or process improvements, disruptive innovations often replace traditional solutions with more efficient or accessible alternatives.
Examples of disruptive innovation:
- Autonomous vehicles: Redefining transportation and logistics.
- Blockchain technology: Revolutionizing finance, supply chains, and secure data sharing.
- AI-driven healthcare tools: Providing faster and more accurate diagnostics than traditional methods.
Impact: Disruptive innovations can reshape industries, sometimes displacing established companies while creating opportunities for startups and early adopters.
Open and Collaborative Innovation
Open innovation leverages external ideas, research, and partnerships to accelerate technological advancement. This approach encourages collaboration between companies, universities, startups, and communities.
Examples of collaborative innovation:
- Open-source software: Linux, Python, and other platforms driving global innovation.
- Tech incubators and accelerators: Providing funding, mentorship, and resources to emerging tech startups.
- Crowdsourcing research: Collaborative projects for AI development, environmental monitoring, or medical breakthroughs.
Impact: Open innovation fosters a culture of shared knowledge and collective problem-solving, often accelerating progress beyond what a single organization could achieve.
Emerging Technology and Future Innovations
The landscape of innovation in technology is evolving faster than ever. Emerging technologies are reshaping industries, creating new opportunities, and fundamentally altering the way we live and work. Let’s explore some of the most impactful innovations driving the future.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are at the forefront of technological innovation. These technologies allow machines to learn, analyze data, and make decisions, opening new possibilities across industries.
Applications of AI and ML:
- Healthcare: AI algorithms assist in diagnosing diseases, predicting patient outcomes, and developing personalized treatment plans.
- Finance: Automated fraud detection, algorithmic trading, and credit scoring.
- Retail: Personalized recommendations, inventory optimization, and predictive analytics.
- Transportation: AI powers autonomous vehicles, traffic management systems, and predictive maintenance.
Impact: According to PwC, AI could contribute up to $15.7 trillion to the global economy by 2030, highlighting its transformative potential. Businesses that adopt AI-driven solutions gain efficiency, accuracy, and competitive advantage.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) connects devices, sensors, and systems, enabling seamless communication and smart decision-making. IoT is revolutionizing both personal and industrial applications.
Examples of IoT innovations:
- Smart homes: Connected thermostats, security systems, and appliances.
- Smart cities: Traffic monitoring, energy-efficient lighting, and waste management.
- Industrial IoT (IIoT): Predictive maintenance, supply chain optimization, and remote monitoring of machinery.
Impact: IoT improves efficiency, safety, and convenience while generating valuable data insights. Gartner predicts there will be over 25 billion connected devices by 2026, emphasizing the rapid expansion of this technology.
Robotics and Automation
Robotics and automation are central to modern technological innovation, transforming manufacturing, services, and daily life.
Applications:
- Industrial robots: Automate repetitive and hazardous tasks in manufacturing.
- Service robots: Assist in healthcare, hospitality, and logistics.
- AI-driven automation: Streamlines business processes, reduces costs, and improves accuracy.
Impact: According to the International Federation of Robotics (IFR), the use of industrial robots is growing at about 13% annually, highlighting how automation is driving global productivity.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
VR and AR are reshaping how we experience entertainment, education, and training.
Applications of VR/AR innovations:
- Gaming and entertainment: Immersive experiences that enhance engagement.
- Education and training: Virtual classrooms, medical simulations, and skill-based learning.
- Professional development: AR overlays for construction, engineering, and maintenance.
Impact: VR/AR technologies are expected to generate over $300 billion in global revenue by 2026, according to Statista, making them a key area of technological innovation.
Sustainable and Green Technology
Innovation in technology is also addressing environmental challenges. Sustainable tech focuses on energy efficiency, resource management, and reducing carbon footprints.
Examples:
- Renewable energy innovations: Solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage solutions.
- Electric vehicles (EVs): Tesla, Rivian, and other companies are leading the EV revolution.
- Sustainable manufacturing: Reducing waste and optimizing resource use in production.
Impact: According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), renewable energy innovations could reduce global carbon emissions by up to 70% by 2050, emphasizing the role of technology in combating climate change.
How Innovation in Technology Impacts Society
The influence of innovation in technology goes far beyond businesses and gadgets—it touches every aspect of society. From economic growth to healthcare, education, and social structures, technological innovation is reshaping our world.
Economic Growth
Technological innovation is a major driver of economic development. By introducing new products, services, and processes, innovations create jobs, industries, and markets that didn’t exist before.
Examples and impacts:
- AI and automation: Create high-demand jobs in software development, data science, and robotics, while increasing productivity across industries.
- Startups and tech entrepreneurship: Emerging companies leveraging innovative technologies drive competition and economic diversification.
- Global competitiveness: Countries investing in innovation maintain leadership in sectors like renewable energy, digital finance, and advanced manufacturing.
Data Point: According to the World Economic Forum, digital innovation contributes approximately $6 trillion annually to the global economy, highlighting its enormous financial impact.
Education and Skill Development
Technological innovation is transforming education, learning, and skill development. Emerging tools make learning more accessible, interactive, and personalized.
Examples:
- Virtual classrooms and e-learning platforms: Platforms like Coursera and Khan Academy make high-quality education accessible worldwide.
- AI tutors and adaptive learning systems: Customize lessons based on individual student performance.
- Skill-based training: VR simulations for healthcare, engineering, and manufacturing improve hands-on training experiences.
Impact: Individuals can acquire future-ready skills, preparing them for emerging industries driven by technology.
Healthcare and Quality of Life
Innovation in technology has dramatically improved healthcare outcomes and overall quality of life.
Key innovations:
- AI diagnostics: Tools that detect diseases like cancer or heart conditions with high accuracy.
- Telemedicine: Expands healthcare access to rural or underserved areas.
- Robotic surgery: Minimizes risks, speeds recovery, and improves precision.
- Wearable devices: Monitor health in real-time, enabling early detection of conditions.
Data Point: A report by McKinsey states that digital health innovations could save $300–$450 billion annually in the U.S. healthcare system by 2025.
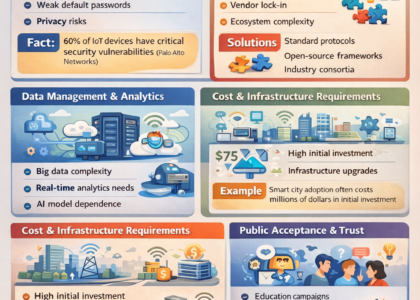
Challenges and Risks of Technology Innovation
While innovation in technology brings tremendous benefits, it also introduces challenges and risks that society must address:
- Ethical concerns: AI bias, privacy violations, and ethical decision-making in automated systems.
- Job displacement: Automation may replace certain roles, requiring reskilling and upskilling.
- Economic inequality: Unequal access to emerging technologies can widen societal gaps.
- Regulation and governance: Governments must balance innovation with safety, security, and fairness.
Example: Facial recognition technology has sparked debates about privacy, bias, and government surveillance, demonstrating the complex social implications of innovation.