Introduction
In today’s digital world, staying informed about tech cybersecurity updates is no longer optional—it’s essential. Cyber threats are evolving rapidly, targeting individuals, businesses, and critical infrastructure. From ransomware and phishing attacks to vulnerabilities in cloud systems and IoT devices, the landscape of cyber threats is constantly changing. Organizations that fail to keep up with the latest cybersecurity trends risk not only financial loss but also reputational damage and regulatory penalties.
Tech cybersecurity updates refer to the latest developments, patches, software updates, and strategies implemented to protect systems and data from cyber threats. These updates often include security patches for software vulnerabilities, firmware improvements for hardware, and advancements in threat detection powered by AI and machine learning.
The goal of this article is to provide a comprehensive guide to tech cybersecurity updates, exploring everything from current trends and emerging threats to best practices and future innovations. Whether you are an IT professional, business leader, or an individual concerned about online security, understanding these updates is critical to staying secure in a digitally connected world.http://futuretechfrontier.com
Understanding Tech Cybersecurity Updates
What is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity refers to the practice of protecting systems, networks, and data from digital attacks. It encompasses a wide range of measures designed to prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and other cyber threats. While often used interchangeably with IT security or network security, cybersecurity is broader, covering software, hardware, networks, and even human behavior.
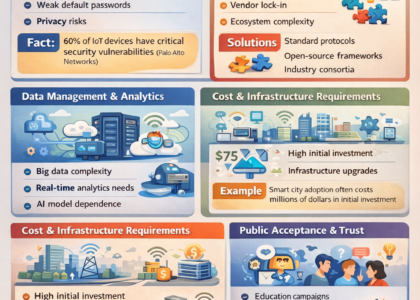
In today’s interconnected world, cybersecurity is crucial not only for businesses but also for individuals. With the rise of cloud computing, mobile devices, and Internet of Things (IoT) networks, vulnerabilities have expanded, making tech cybersecurity updates more important than ever.
Importance of Tech Cybersecurity Updates
Keeping systems updated is one of the most effective ways to defend against cyber threats. Cybercriminals exploit outdated software, unpatched vulnerabilities, and weak security configurations to gain unauthorized access.
Key reasons tech cybersecurity updates are vital:
- Preventing Data Breaches: Outdated systems are easier to infiltrate, leading to stolen customer data, financial loss, and reputational damage.
- Defense Against Ransomware and Malware: Cybersecurity patches and updates close loopholes that ransomware and malware exploit.
- Compliance and Legal Requirements: Regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA require organizations to implement proper cybersecurity measures.
- Business Continuity: Keeping systems secure ensures operations remain uninterrupted and prevents costly downtime.
Fact: According to a report by IBM Security, the average cost of a data breach in 2025 was $4.45 million, making regular security updates critical for businesses of all sizes.
How Cybersecurity Updates Work
Cybersecurity updates are mechanisms through which organizations and individuals patch vulnerabilities, enhance defenses, and implement new security features. These updates can include:
- Software Patches: Fixing vulnerabilities in operating systems, applications, and security software.
- Firmware and Hardware Updates: Improving security features in routers, IoT devices, and servers.
- Security Policy Updates: Adjusting access controls, password policies, and firewall configurations.
- Threat Intelligence Updates: Incorporating the latest information about emerging threats into security systems.
Updates can be automatic or manual, depending on the system and organization policies. For example, operating systems like Windows and macOS often provide automatic security updates, while enterprise systems may require scheduled manual patching to ensure compatibility and stability.
Case Study: In 2021, the Microsoft Exchange Server vulnerability affected hundreds of thousands of organizations worldwide. Companies that applied cybersecurity updates promptly were protected from widespread breaches, highlighting the importance of timely updates in preventing major security incidents.
Current Cybersecurity Trends and Updates
Staying ahead of cyber threats requires understanding the latest trends in tech cybersecurity updates. From AI-driven defense systems to cloud security enhancements, the landscape is constantly evolving. Here’s an in-depth look at the most significant updates and trends in 2026.
AI and Machine Learning in Cybersecurity
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are revolutionizing cyber defense. By analyzing massive datasets in real-time, AI can detect anomalies, predict attacks, and respond faster than traditional methods.
Key applications:
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): AI monitors network traffic to detect suspicious behavior.
- Anomaly Detection: ML models identify unusual patterns that may indicate breaches.
- Automated Threat Response: AI can isolate compromised systems and prevent malware spread.
Example: Darktrace, an AI cybersecurity platform, uses self-learning algorithms to detect and neutralize threats without human intervention.
Impact: According to Gartner, AI adoption in cybersecurity is expected to grow by 30% annually, demonstrating its critical role in modern defense strategies.
Cloud Security Updates
With more organizations migrating to cloud environments, cloud security updates are essential to protect sensitive data. Cloud systems are vulnerable to misconfigurations, unauthorized access, and advanced attacks.
Latest cloud security measures:
- Encryption enhancements for data at rest and in transit
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) across cloud services
- Automated monitoring tools for unusual access or activity
Fact: The Cloud Security Alliance reports that over 80% of cloud security incidents result from misconfigurations, highlighting the importance of regular updates and monitoring.
Ransomware and Malware Updates
Ransomware remains one of the most dangerous cyber threats, encrypting critical data and demanding payments. Regular updates are crucial to patch vulnerabilities and prevent malware infections.
Current strategies:
- Endpoint security updates to prevent malware execution
- Backup systems and disaster recovery plans
- Threat intelligence feeds to stay ahead of emerging ransomware strains
Case Study: The Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack in 2021 caused major fuel shortages in the U.S. Companies that applied timely cybersecurity updates avoided similar disruptions.
Mobile and IoT Security Updates
Mobile devices and IoT systems are increasingly targeted by cybercriminals. Updates for these platforms are essential to secure personal and enterprise data.
Recent updates include:
- Patch management for smartphones to fix OS vulnerabilities
- IoT firmware updates to prevent unauthorized device access
- Secure communication protocols for connected devices
Impact: As IoT adoption grows, Gartner predicts over 25 billion connected devices by 2026, making regular cybersecurity updates vital to maintain security at scale.
Regulatory and Compliance Updates
Regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA require organizations to maintain updated cybersecurity practices. Compliance updates often include:
- Enhanced data protection policies
- Regular audits and reporting
- Security certifications and standards adoption (ISO 27001, NIST)
Fact: Non-compliance with cybersecurity regulations can result in fines up to $20 million or 4% of global revenue, emphasizing the importance of keeping systems updated.
Emerging Threats and Challenges in Cybersecurity
As technology evolves, cybercriminals continuously develop new methods to exploit vulnerabilities. Staying ahead of these threats requires understanding the latest challenges and implementing timely tech cybersecurity updates.
Social Engineering and Phishing Attacks
Social engineering remains one of the most effective methods for cybercriminals to compromise systems. Phishing attacks manipulate individuals into revealing sensitive information, clicking malicious links, or installing malware.
Recent trends in phishing attacks:
- Spear phishing: Highly targeted attacks using personal or organizational data
- Voice phishing (vishing) and SMS phishing (smishing): Exploiting phone and text communications
- Deepfake attacks: AI-generated voices or videos tricking employees into transferring funds or sharing credentials
Prevention strategies:
- Regular security awareness training
- Email filtering and anti-phishing software
- Continuous updates to security protocols to detect new phishing techniques
Fact: According to Verizon’s 2025 Data Breach Investigations Report, over 80% of breaches involved phishing attacks, highlighting the critical need for proactive updates and training.
Supply Chain Cybersecurity Risks
Supply chain attacks target software vendors, hardware manufacturers, and service providers to compromise multiple organizations at once. These attacks exploit weak links in interconnected systems.
Recent examples:
- SolarWinds attack (2020): Affected thousands of organizations globally through compromised software updates
- Nvidia and other hardware vendor breaches: Exposed sensitive intellectual property and customer data
Updates and defenses:
- Regularly audit third-party vendors for compliance
- Implement segmented network access to limit potential exposure
- Stay informed of vendor-issued security patches and updates
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
APTs are sophisticated, targeted cyber attacks that infiltrate systems and remain undetected for long periods. Unlike opportunistic attacks, APTs are carefully planned to steal sensitive data or disrupt operations.
Characteristics:
- Long-term presence in networks
- Highly targeted against organizations or governments
- Often state-sponsored or highly organized
Defense strategies:
- Continuous network monitoring and anomaly detection
- AI-powered threat intelligence systems
- Regular cybersecurity updates to close vulnerabilities
Insider Threats and Human Factors
Not all threats come from external actors. Insider threats arise when employees, contractors, or business partners intentionally or unintentionally compromise security.
Examples:
- Data leaks due to careless handling of sensitive information
- Unauthorized access from disgruntled employees
- Accidental introduction of malware or ransomware
Mitigation strategies:
- Implement role-based access controls
- Conduct regular training and awareness programs
- Monitor systems for unusual activity and apply real-time updates to access protocols
Best Practices for Staying Updated on Cybersecurity
Keeping systems, networks, and devices secure requires more than just awareness—it demands proactive action and regular tech cybersecurity updates. Implementing best practices ensures organizations and individuals remain resilient against evolving threats.
Automated Updates and Patch Management
Automated updates are one of the simplest yet most effective ways to maintain security. Many operating systems, software applications, and security tools provide automatic updates to patch vulnerabilities as soon as they are discovered.
Best practices:
- Enable automatic updates for all devices and software
- Maintain a regular patch management schedule for enterprise systems
- Prioritize critical security patches to address high-risk vulnerabilities
Fact: According to Ponemon Institute, organizations that implement automated patch management reduce the risk of successful cyber attacks by up to 50%, highlighting its crucial role in cybersecurity.
Cybersecurity Awareness and Training
Employees are often the first line of defense against cyber threats. Regular training programs help staff recognize phishing attempts, social engineering tactics, and malware threats.
Effective training strategies:
- Conduct quarterly cybersecurity workshops
- Simulate phishing attacks to test employee awareness
- Provide up-to-date guidance on handling sensitive data and reporting suspicious activity
Example: Companies that invest in cybersecurity awareness report 60% fewer successful phishing attacks, demonstrating the value of human vigilance alongside tech updates.
Monitoring and Threat Intelligence
Continuous monitoring and threat intelligence allow organizations to stay informed about emerging threats. Real-time alerts and actionable intelligence help prevent attacks before they escalate.
Tools and strategies:
- Threat intelligence feeds from vendors like IBM X-Force or FireEye
- SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) platforms for centralized monitoring
- Regular vulnerability scanning and penetration testing
Benefit: Combining automated updates with threat intelligence ensures proactive defense, reducing downtime and minimizing potential breaches.
Partnering with Cybersecurity Experts
Organizations can strengthen defenses by working with Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs) or consulting cybersecurity experts. These partnerships provide access to:
- Up-to-date knowledge of emerging threats
- Expertise in patching and vulnerability management
- Support for regulatory compliance and audits
Case Study: A multinational financial firm partnered with an MSSP to monitor its network 24/7. As a result, attempted ransomware attacks were detected and neutralized in real-time, preventing data loss and downtime.
The Future of Tech Cybersecurity Updates
As technology continues to advance, the field of cybersecurity is evolving at an unprecedented pace. Tech cybersecurity updates of the future will not only respond to threats but also anticipate and prevent attacks proactively. Here’s what we can expect in the coming years.
Predictive Security Using AI
Artificial intelligence is moving beyond detection and response toward predictive security. AI systems analyze patterns, historical data, and user behavior to forecast potential threats before they occur.
Applications:
- Predictive threat modeling: Identifies vulnerabilities before they are exploited
- Behavioral analysis: Detects deviations from normal patterns indicating potential breaches
- Automated countermeasures: AI can automatically block suspicious activities in real-time
Impact: Organizations that adopt predictive AI can reduce incident response time by over 70%, creating a proactive cybersecurity posture.
Blockchain in Cybersecurity
Blockchain technology offers a secure, decentralized way to store and share data, making it resistant to tampering and hacking.
Use cases in cybersecurity:
- Data integrity verification: Ensures files and records are authentic
- Secure transactions: Reduces fraud in financial and digital asset transfers
- Identity management: Blockchain-based digital IDs protect personal and enterprise data
Example: Several fintech startups are integrating blockchain to secure payment networks and prevent data breaches.
Quantum Computing and Security Challenges
Quantum computing promises massive computational power, but it also introduces risks to traditional encryption methods. Hackers could potentially break current encryption algorithms, compromising sensitive data.
Cybersecurity updates in response:
- Development of quantum-resistant encryption protocols
- Updating critical systems to quantum-safe algorithms
- Research initiatives from NIST and leading tech companies
Fact: Cybersecurity experts predict that by 2030, quantum-resistant encryption will be mandatory for protecting sensitive government and financial data.
Integration Across Industries
Future cybersecurity updates will be industry-specific, addressing unique threats in sectors like finance, healthcare, manufacturing, and critical infrastructure.
Examples:
- Healthcare: AI-driven monitoring and patient data encryption
- Finance: Real-time fraud detection and blockchain-secured transactions
- Critical infrastructure: Industrial control systems protected with predictive threat intelligence
Impact: Sector-specific updates ensure that cybersecurity measures are tailored, effective, and future-proof against emerging threats.